Content

This means that it uses less fixed assets to support its core business while sustaining a lower gross margin. Total leverage measures the sensitivity of earnings to changes in the level of a company’s sales. When evaluating the riskiness of leverage it is also important to factor in the value of the company itself and its activities. If a company borrows money to modernize, add to its product line, or expand internationally, the additional diversification will likely offset the additional risk from leverage. The upshot is, if value is expected to be added from the use of financial leverage, the added risk should not have a negative effect on a company or its investments. If earnings before interest and taxes are greater than the cost of financial leverage than the increased risk of leverage will be worthwhile. For instance, with the debt-to-equity ratio — arguably the most prominent financial leverage equation — you want your ratio to be below 1.0.
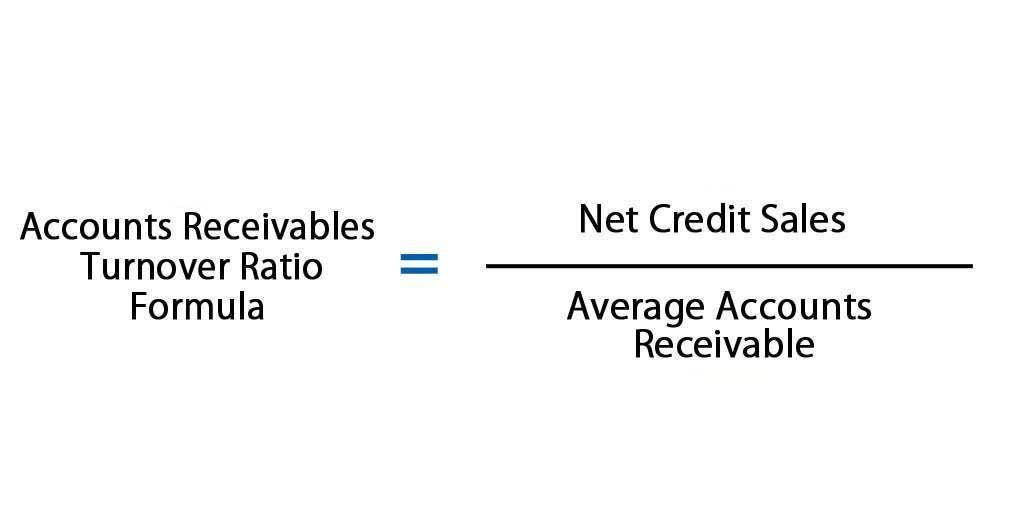
By breaking down the equation, you can see that DOL is expressed by the relationship between quantity, price and variable cost per unit to fixed costs. If operating income is sensitive to changes in the pricing structure and sales, the firm is expected to generate a high DOL and vice versa. However, once those investments started paying off, Verizon’s financial leverage ratio leveled out and returned to a lower, more reassuring figure. A higher financial leverage ratio indicates that a company is using debt to finance its assets and operations — often a telltale sign of a business that could be a risky bet for potential investors. However, it is negative when the company’s profits are less than the cost of insuring the funds. Leverage is an essential source of capital to support limited shareholder investments.
What Is A Degree Of Financial Leverage Dfl?
Therefore, companies with extremely volatile operating incomes should not take on substantial leverage because there is a high probability of financial distress for the business. This formula can be even used to compare data of many companies that can help an investor in deciding which company to invest in, based on the result of how much risk is attached with each companies capital structure. This ratio indicates that the higher the degree of financial leverage, the more volatile earnings will be. Since interest is usually a fixed expense, leverage magnifies returns, and EPS. This is good when operating income is rising, but it can be a problem when operating income is under pressure.

The main objective is to determine the indifferent points of EBIT among a range of various financing plans that a company would choose. Whenever the percentage change in EPS as a result of the percentage change in EBIT is greater than the percentage change in EBIT or it is greater than 1; thus, financial leverage exists. The annual dividends on the preferred stocks are $2,400 (1,000 shares × $4). Therefore, a 1% change in ABC Ltd’s leverage will change its operating income by 1.22%. Therefore, a 1% change in the XYZ Ltd’s leverage will change its operating income by 1.11%.
Degree Of Financial Leverage Dfl
Leverage is a financial ratio of a Company’s debt or borrowed capital to its equity capital. Leveraging is a strategy of borrowing money for a company’s operations, assuming that the returns from the operations will be higher than the cost of the borrowed capital.
- Leverage helps to forecast future cash flows and do a risk assessment.
- Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase.
- The main objective is to determine the indifferent points of EBIT among a range of various financing plans that a company would choose.
- From this calculation to derive Macy’s equity multiplier we see that the company’s assets are funded by liabilities worth $15.53 billion.
Therefore, the company has the potential for higher profits when EBIT increases, but it also takes on more risk that it will not be able to cover its fixed financing costs if EBIT is too low. If the company uses more debt than equity, the higher will be the financial leverage ratio. A way to assess a firm’s ability to utilize its debts to acquire more assets that is expected to generate a bigger income compared to their cost of borrowing it, is to compute for their debt to capital ratio. A leverage ratio can also be used to estimate how changes in output will affect operating income by measuring a company’s mix of operating expenses. Both financial and operating leverage emerge from the base of fixed costs. That’s to say, operating leverage appears where there is a fixed financial charge . To conclude, financial leverage emerges as a result of fixed financial cost (interest on debentures and bonds + preference dividend).
Low Vs High Financial Leverage
Enterprise Value Formula and Definition – CFA Level I & II Fundamentals A company’s enterprise value is an important point of understanding for investors and is a fundamental learning point in many business schools, as well… The dividend payout ratio is the measure of dividends paid out to shareholders relative to the company’s net income. EBITDA, or earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization, is a measure of a company’s overall financial performance.
Operating And Financial Leverage Operating And Financial Leverage Content What Is Financial Leverage? Formula For Degree Of Financial Leverage Microsoft Currently Has An Annual Coupon Bond Outstanding A Decrease In The Market Rate Of Interest… https://t.co/rqbRNGlhVJ
— Aline Mateo (@mateo_aline) December 8, 2021
On the other hand, almost half of Lehman’s balance sheet consisted of closely offsetting positions and very-low-risk assets, such as regulatory deposits. On that basis, Lehman held $373 billion of “net assets” and a “net leverage ratio” of 16.1. This is not a standardized computation, but it probably corresponds more closely to what most people think of when they hear of a leverage ratio. Work on Basel II began in the early 1990s and it was implemented in stages beginning in 2005. Basel II attempted to limit economic leverage rather than accounting leverage. It required advanced banks to estimate the risk of their positions and allocate capital accordingly. While this is much more rational in theory, it is more subject to estimation error, both honest and opportunitistic.
Why Organizations Leverage Finances
Since interest is usually a fixed expense, leverage magnifies returns and EPS. The use of financial leverage varies greatly by industry and by the business sector.

Degree of Operating Leverage – CFA Level 1 The term degree of operating leverage does not get as much attention as its more forthright cousin, financial leverage, but is just as important… As can be seen in the formula below, the DFL at Walmart based on 2019 figures can be calculated as 1.12x or 112%. This means that for each 1% percentage change in operating income, net income will increase by 1.12% (which is 1.12x or 112% of 1%). The degree of financial leverage is not to be confused with the more popular balance sheet metric, financial leverage. While they have strong similarities both calculating risk (and reward!) from the use of debt, they go about measuring that risk in two different ways.
The DFL formula measures the change in net income when the operating result changes by 1% . The output of the DFL formula can be read as “for every 1% change in the operating result, the net result changes by X%”. This relationship shows that the higher the level of financial leverage, the more volatile the returns.
How To Use Enterprise Value To Compare Companies
For outsiders, it is hard to calculate operating leverage as fixed and variable costs are usually not disclosed. The effect of financial leverage leverage is measured by subtracting the economic rate of return after corporate tax is deducted from the return on equity.
What if degree of combined leverage is negative?
When interest exceeds operating profit, the firm is showing a net loss and DFL is negative. This negative DFL means that an increase in operating profit will lead to a decrease in the firm’s net loss and vice versa.
The interest was charged at 5% on an outstanding debt of $1,000,000, and taxes paid was $25,000. Let us take the example of Company XYZ Ltd, which has clocked net income of $400,000 in the current year vis-à-vis $300,000 in the previous year. In the current year, the interest expense and taxes of the company stood at $59,000 and $100,000 respectively, while in the previous year it stood at $40,000 and $90,000 respectively. And taxes to the net income, all of which are line items from the income statement. Then, calculate the percentage change in EBIT by subtracting the EBIT of the previous year from that of the current year and then dividing the result by the EBIT of the previous year.
The degree of total leverage is a ratio that compares the rate of change in a company’s earnings per share to a change in its revenues from sales. Another way to calculate this ratio is to multiply the degree of operating leverage with the degree of financial leverage. A degree of financial leverage is a leverage ratio that measures the sensitivity of a company’s earnings per share to fluctuations in operating profit as a result of changes in its capital structure. The degree of financial leverage measures the percentage change in earnings per share for a change in operating profit, also known as earnings before interest and taxes . The degree of financial leverage is a financial ratio that measures the sensitivity in fluctuations of a company’s overall profitability to the volatility of its operating income caused by changes in its capital structure. It is the relationship between percentage change in earnings per share and the percentage change in earnings before interest and tax . If the Degree of Financial Leverage is high, the Earnings Per Share or EPS would be more unpredictable while all other factors would remain the same.
So, in the case of an economic downturn, their earnings may plummet because of their high fixed costs and low sales. John’s Software is a leading software business, which mostly incurs fixed costs for upfront development and marketing. John’s fixed costs are $780,000, which goes towards developers’ salaries and the cost per unit is $0.08. Given that the software industry is involved in the development, marketing and sales, it includes a range of applications, from network systems and operating management tools to customized software for enterprises. If the percentage change in earnings and the percentage change in sales are both known, a company can simply divide the percentage change in earnings by the percentage change in sales to determine total leverage. Due to financial leverage’s effect on solvency, a company that borrows too much money might face bankruptcy during a business downturn, while a less-levered company may avoid bankruptcy due to higher liquidity.
Operational risk is the analyzing of company operating income due to change in sale. Financial risk is the analying of company EPS change due to change in operating income. Despite how similar it is to the debt to EBITDA leverage ratio, they are actually two distinct ratios with their only difference being that EBITDAX is EBITDA excluding exploration costs. Normally needed by most credit institutions, debt to EBITDA leverage ratio shows the level that a firm is likely to fail when it comes to paying their liabilities.
This means that it uses more fixed assets to support its core business. It also means that the company can make more money from each additional sale while keeping its fixed costs intact. So, the company has a high DOL by making fewer sales with high margins.
- Though high DFLs are more risky than low DFLs, high DFLs are more advantageous when sale volume is high than low DFLs.
- Sources of financial leverage are primarily debt and preferred stock.
- On the other hand, companies with high DFLs must generate more income during a period to break even because they must pay more fixed financial costs.
- Financial risk is the analying of company EPS change due to change in operating income.
- If, in contrast, a company’s operations provide a better rate of return than the interest rate on the loans it has incurred, debt may be used to fuel the expansion of the business.
- It measures the extent to which a company uses borrowings to earn a higher income and increase its assets.
- The debt to equity ratio plays a role in the working average cost of capital as well, as the overall interest on financing represents the break-even point that must be obtained to achieve profitability in a given venture.
The use of financial levers varies greatly depending on the industry and industry. There are many industrial sectors in which companies operate with a high degree of financial leverage. Retail stores, airlines, supermarkets, utilities, and banking institutions are classic examples. Unfortunately, the excessive use of financial leverage by many companies in these sectors has played an important role in forcing many of them to file for Chapter 11 bankruptcy. Degree of combined leverage is the combination of both operational and financial leverage. DCL shows us the best combination of operational and financial leverage that is used in the company. The more fixed financing costs a company has, the more its net income will increase as earnings before interest and taxes change.
What is financial management class 12th business studies?
The financial management role is the sizing and composition of the fixed assets, amount and composition of the current assets, fixing the debt-equity ratio in the capital, deciding on the long and short term financing, and all the items in the profit and loss account.
And instead of treating it as an outright expense, operating leases are treated as amortizable investments. There are businesses that need larger capital expenditures such as those in the manufacturing and utility industries which would need to have more loans secured compared to other kinds of companies. Numerous forms of capital requirements and minimum reserves exist which are implemented on banks in America by the Comptroller of the Currency and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. The fusion of Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation protection with fractional reserve banking has resulted in a banking environment with low lending risks. In the United States, banks are one of the most leveraged or indebted institutions.
- Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology.
- As a result, fixed assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, acquire a higher value without incurring higher costs.
- Financial leverage is the ratio of a company’s equity to financial debt.
- Taking on debt, as an individual or a company, will always bring about a heightened level of risk due to the fact that income must be used to pay back the debt even if earnings or cash flows go down.
- The degree of financial leverage is an important indicator to measure the relative changes of EPS compare to changes in EBIT.
- To get comfortable with the formula and add some real-life perspective, let’s now look at the degree of financial leverage with retail giant Walmart.
- The notional amount of the swap does count for notional leverage, so notional leverage is 2 to 1.
Interest payments on fixed-income securities are fixed and affect the EPS . Thus, the fluctuation of EPS varies to a greater extent than fluctuation of EBIT. This is because interest expense and preferred dividends are fixed no matter the level of EBIT. If EBIT increases, interest and preferred dividends do no increase proportionately and hence net income increases by a different percentage. Degree of financial leverage is a measure that assesses how sensitive a company’s net income is to a change in the company’s operating income. It is calculated by dividing percentage change in earnings per share by percentage change in earnings before interest and taxes . A high degree of financial leverage indicates that even a small change in the company’s leverage may result in a significant fluctuation in the company’s profitability.
This situation encourages the finance manager to go in for more and more debt financing to enhance the benefits to shareholders. To calculate both operating leverage and financial leverage, EBIT is referred to as the linking point in the study of leverage. When calculating the operating leverage, EBIT is a dependant variable that is determined by the level of sales.
Leverage Ratio: Formula & 9 Variations – Seeking Alpha
Leverage Ratio: Formula & 9 Variations.
Posted: Thu, 11 Nov 2021 08:00:00 GMT [source]
To calculate the Degree of Financial Leverage , The degree of financial leverage is a metric that measures the sensitivity of a company’s operating income due to changes in its capital structure. It is important to understand the concept of the degree of financial leverage because it indicates the relationship between the capital structure of a company and its operating income. On the other hand, a high ratio indicates a higher percentage of debt in a company’s capital structure, and these companies are vulnerable because their net income is more responsive to fluctuations in operating income. Degree of financial leverage is essential for companies to understand how operational costs, liabilities and expenses affect revenue and income. Managers use operating leverage to calculate a firm’sbreakeven pointand estimate the effectiveness of pricing structure. An effective pricing structure can lead to higher economic gains because the firm can essentially control demand by offering a better product at a lower price.